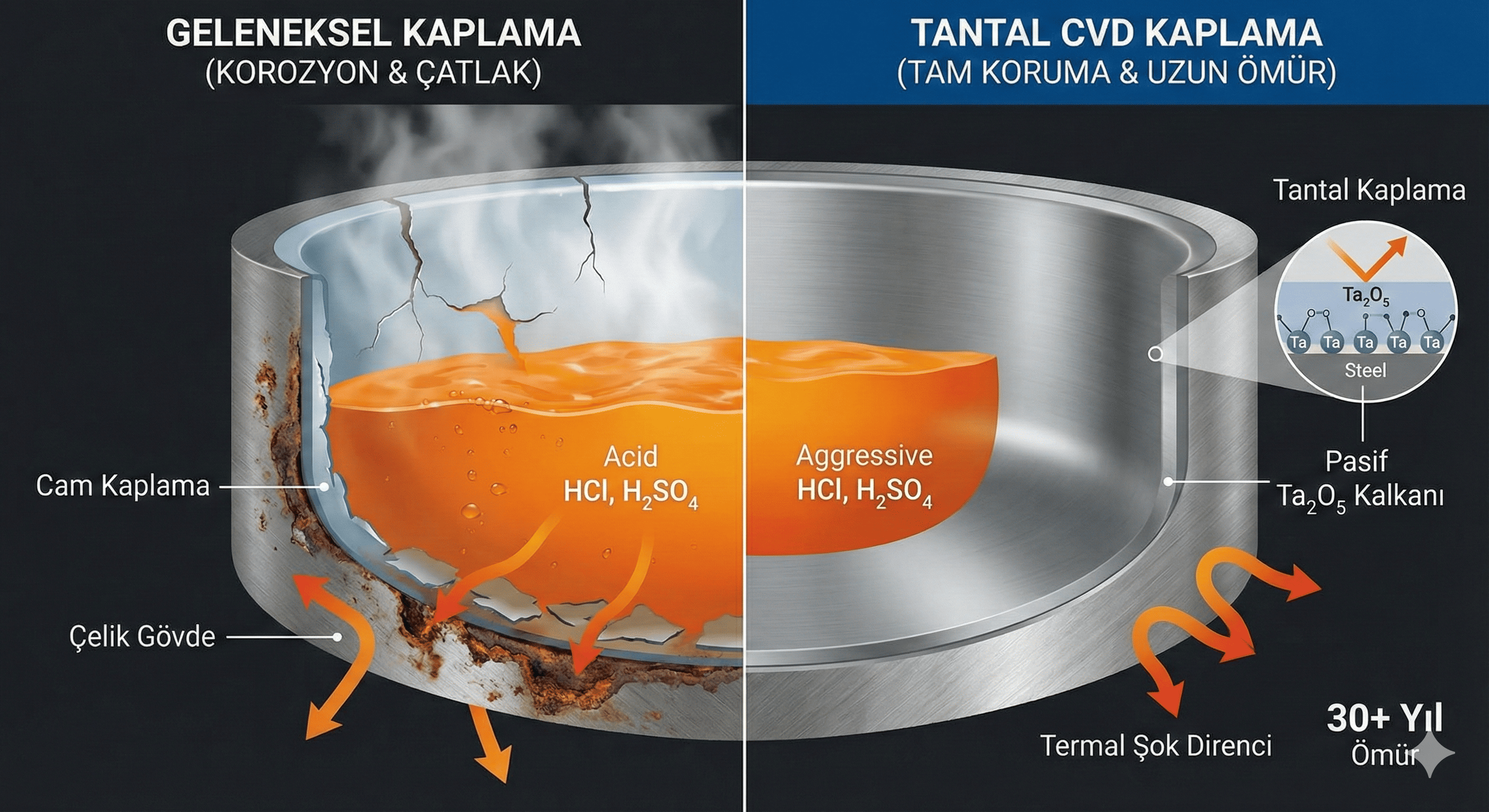
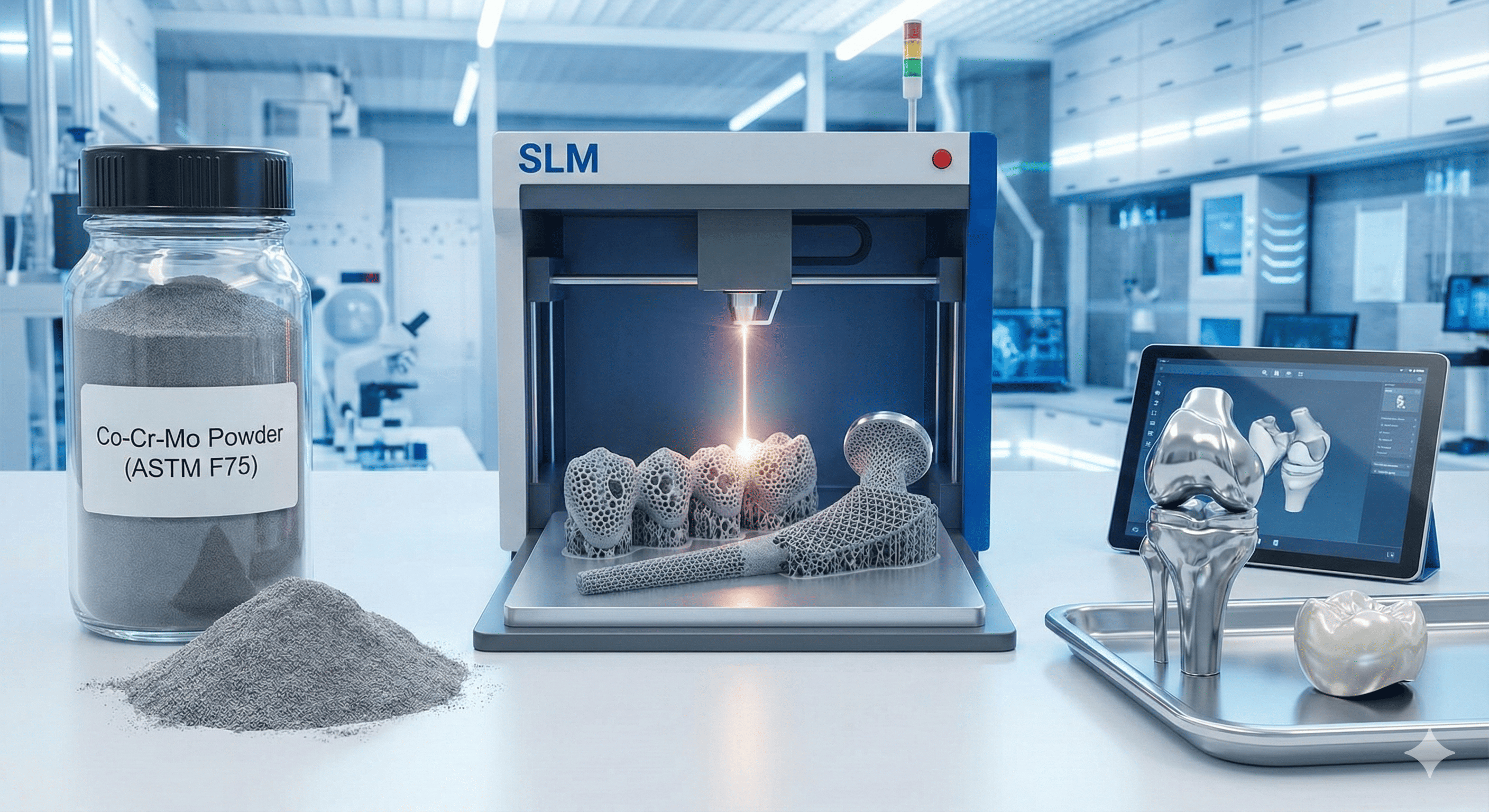
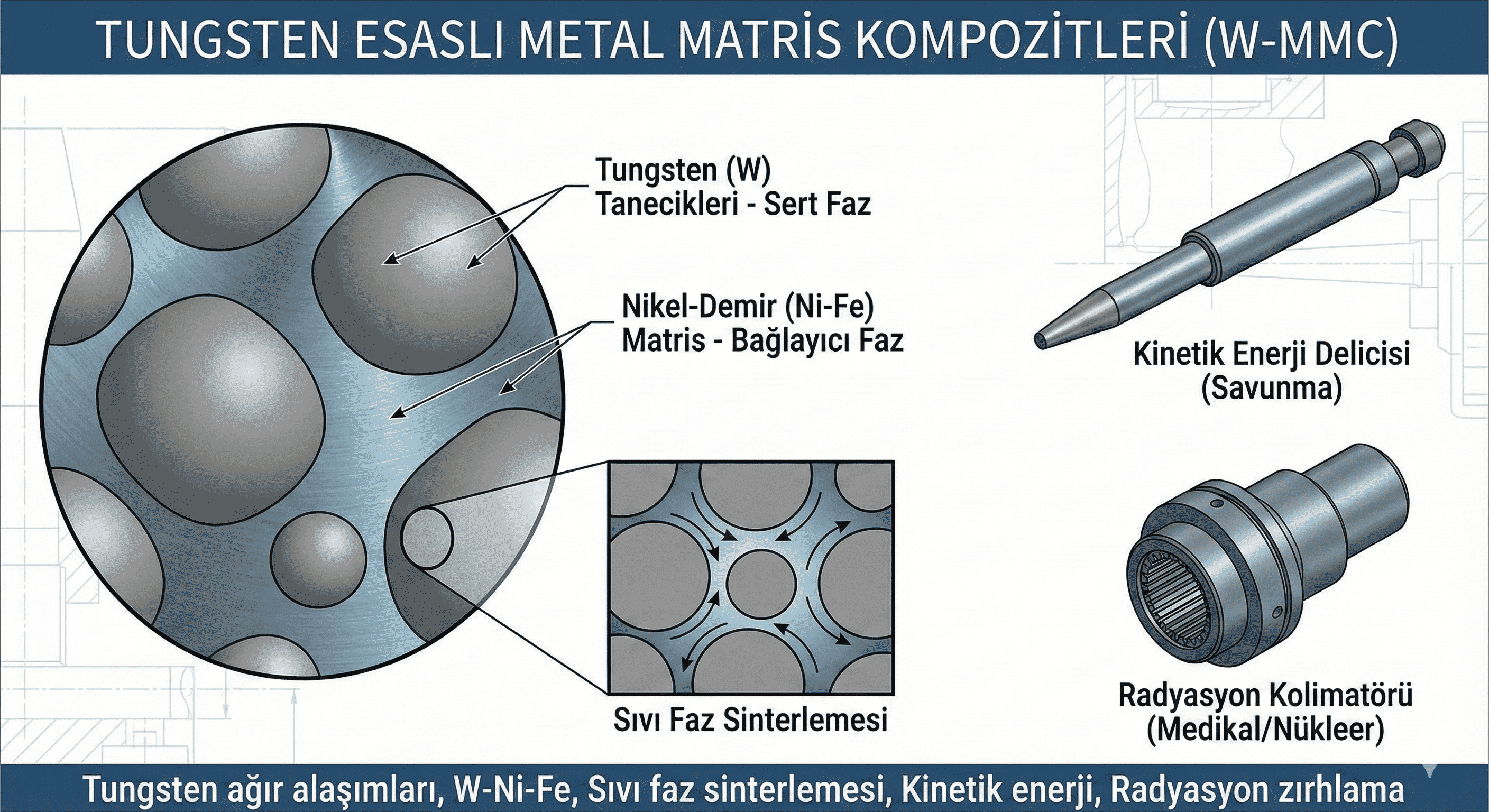
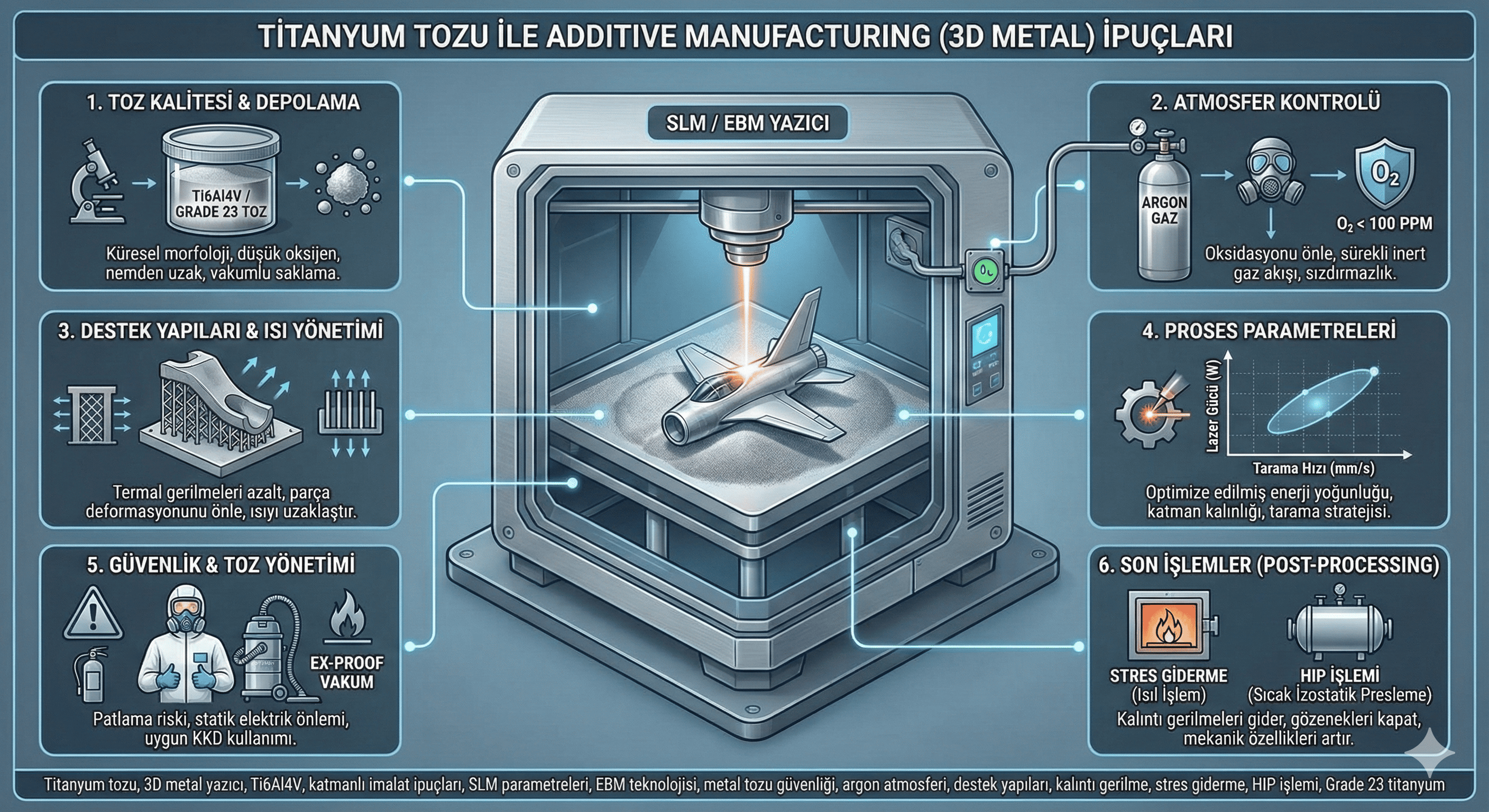
Indium oxide (In²O³) nanoparticles are notable for their diverse applications and unique physical and chemical properties. This article provides an in-depth review of the synthesis methods, structural and functional properties, and a wide range of applications of In²O³ nanoparticles. Challenges related to their use and potential future directions for research are also discussed.
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview of Indium Oxide Nanoparticles
- Definition and general characteristics of indium oxide nanoparticles.
- The significance of In²O³ as a semiconductor and its role in nanotechnology.
1.2. Significance in Nanotechnology
- Unique properties of In²O³ nanoparticles compared to their bulk counterparts.
- Overview of their potential applications in various fields due to these properties.
1.3. Objectives of the Article
- To explore the synthesis methods, properties, and applications of In²O³ nanoparticles.
- To identify challenges and propose future research directions.
2. Synthesis of Indium Oxide Nanoparticles
2.1. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- Description of the CVD method for synthesizing In²O³ nanoparticles.
- Key parameters: temperature, pressure, and gas composition.
2.2. Sol-Gel Method
- Overview of the sol-gel process for preparing In²O³ nanoparticles.
- Steps involved: sol formation, gelation, drying, and calcination.
2.3. Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Methods
- Explanation of hydrothermal and solvothermal techniques.
- Influence of pressure, temperature, and precursors on nanoparticle size and morphology.
2.4. Co-precipitation Method
- Use of co-precipitation to produce In²O³ nanoparticles.
- Factors affecting the process, such as pH, concentration, and temperature.
2.5. Other Methods
- Brief discussion of alternative synthesis methods, including microwave-assisted synthesis and thermal decomposition.
3. Properties of Indium Oxide Nanoparticles
3.1. Structural Properties
- Crystallinity, size, and morphology of In²O³ nanoparticles.
- Characterization techniques: X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
3.2. Optical Properties
- Optical absorption, photoluminescence, and emission characteristics.
- Applications in optical devices and sensors.
3.3. Electronic Properties
- Electrical conductivity and semiconducting behavior.
- Comparison with bulk In²O³ and implications for electronic applications.
3.4. Catalytic Properties
- Catalytic activity of In²O³ nanoparticles in various reactions.
- Use in environmental catalysis and industrial processes.
4. Applications of Indium Oxide Nanoparticles
4.1. Electronics and Semiconductors
- Application in thin-film transistors and touch screens.
- Role in gas sensors and transparent conductive films.
4.2. Optoelectronics
- Use in displays, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and photovoltaic devices.
- Application in optical coatings and smart windows.
4.3. Biomedical Applications
- Potential use in imaging, drug delivery systems, and biosensing.
- Evaluation of biocompatibility and safety.
4.4. Energy and Environmental Applications
- Application in energy storage systems, such as batteries and supercapacitors.
- Use in environmental remediation and as catalysts for pollutant degradation.
5. Challenges and Limitations
5.1. Synthesis Challenges
- Difficulties in achieving uniform particle size and morphology.
- Scalability and reproducibility of synthesis methods.
5.2. Stability and Reactivity
- Stability of In²O³ nanoparticles under various environmental conditions.
- Methods for enhancing stability and controlling surface reactivity.
5.3. Cost and Environmental Impact
- Economic considerations of production and use.
- Environmental impact and strategies for minimizing ecological footprint.
5.4. Regulatory and Safety Concerns
- Compliance with regulations governing the use of nanomaterials.
- Safety protocols for handling and disposal of nanoparticles.
6. Future Directions
6.1. Advancements in Synthesis Techniques
- Innovations to improve control over size, shape, and properties.
- Exploration of new synthesis methods and materials.
6.2. Emerging Applications
- Novel applications in technology, medicine, and energy.
- Potential for interdisciplinary research and development.
6.3. Interdisciplinary Collaboration
- Importance of collaboration between chemists, materials scientists, and engineers.
- Examples of successful interdisciplinary projects and research.
7. Conclusion
7.1. Summary of Key Findings
- Recap of synthesis methods, properties, and applications of In²O³ nanoparticles.
7.2. Impact on Technology and Science
- Overall significance of indium oxide nanoparticles in advancing various fields.
7.3. Final Thoughts
- Reflection on the future potential and ongoing research in indium oxide nanoparticles.
8. References
- Comprehensive list of scientific papers, reviews, and sources cited in the article.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of indium oxide nanoparticles. If you have specific data, case studies, or additional sections you’d like to include, please let me know!